Today we will learn how to convert String to byte array in java. We will also learn how to convert byte array to String in Java.
String to byte array
We can use String class getBytes() method to encode the string into a sequence of bytes using the platform’s default charset. This method is overloaded and we can also pass Charset as argument. Here is a simple program showing how to convert String to byte array in java.
package com.journaldev.util;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class StringToByteArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "PANKAJ";
byte[] byteArr = str.getBytes();
// print the byte[] elements
System.out.println("String to byte array: " + Arrays.toString(byteArr));
}
}
Below image shows the output when we run the above program.  We can also get the byte array using the below code.
We can also get the byte array using the below code.
byte[] byteArr = str.getBytes("UTF-8");
However if we provide Charset name, then we will have to either catch UnsupportedEncodingException exception or throw it. Better approach is to use StandardCharsets class introduced in Java 1.7 as shown below.
byte[] byteArr = str.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
That’s all the different ways to convert String to byte array in java.
Java byte array to String
Let’s look at a simple program showing how to convert byte array to String in Java.
package com.journaldev.util;
public class ByteArrayToString {
public static void main(String[] args) {
byte[] byteArray = { 'P', 'A', 'N', 'K', 'A', 'J' };
byte[] byteArray1 = { 80, 65, 78, 75, 65, 74 };
String str = new String(byteArray);
String str1 = new String(byteArray1);
System.out.println(str);
System.out.println(str1);
}
}
Below image shows the output produced by the above program. 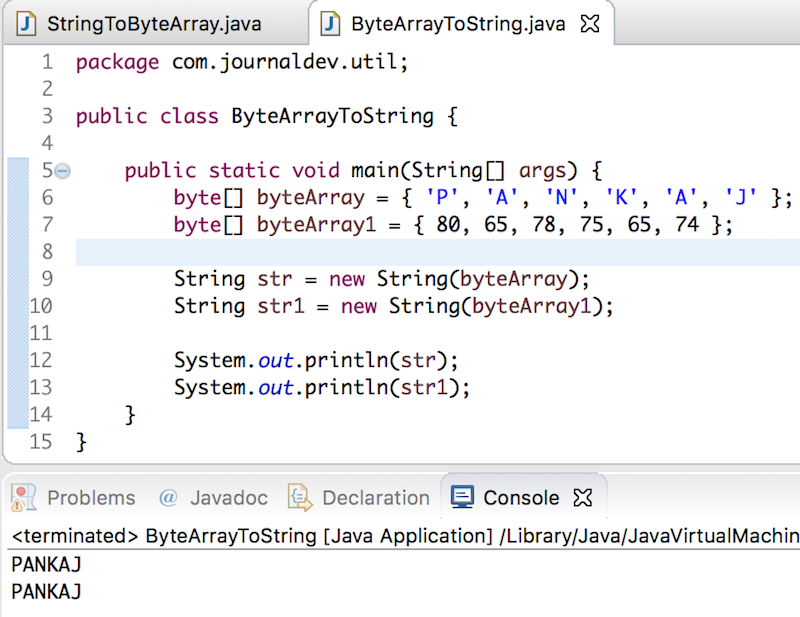 Did you notice that I am providing char while creating the byte array? It works because of autoboxing and char ‘P’ is being converted to 80 in the byte array. That’s why the output is the same for both the byte array to string conversion. String also has a constructor where we can provide byte array and Charset as an argument. So below code can also be used to convert byte array to String in Java.
Did you notice that I am providing char while creating the byte array? It works because of autoboxing and char ‘P’ is being converted to 80 in the byte array. That’s why the output is the same for both the byte array to string conversion. String also has a constructor where we can provide byte array and Charset as an argument. So below code can also be used to convert byte array to String in Java.
String str = new String(byteArray, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
String class also has a method to convert a subset of the byte array to String.
byte[] byteArray1 = { 80, 65, 78, 75, 65, 74 };
String str = new String(byteArray1, 0, 3, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
Above code is perfectly fine and ‘str’ value will be ‘PAN’. That’s all about converting byte array to String in Java.
You can checkout more array examples from our GitHub Repository.
Reference: getBytes API Doc
Thanks for learning with the DigitalOcean Community. Check out our offerings for compute, storage, networking, and managed databases.
While we believe that this content benefits our community, we have not yet thoroughly reviewed it. If you have any suggestions for improvements, please let us know by clicking the “report an issue“ button at the bottom of the tutorial.

What is the use (some real-time application usage) of converting a string into a byte array?
- B Ekam
One example is processing the byte array for cryptography algorithms. To encrypt or decrypt a text you need to do calculations on individual bytes.
- RJ
To read and write on sockets we need a byteArray, so while writing on socket, convert your string into byteArray and write it on outStream, while reading from socket, read from inuptStream into a byteArray and convert it into string, if needed.
- Chaitanya Bhalerao
good night , can you tell me if the code from string array list to byte array list
- monika
how to read a binary file and write in a text file or xml file using java
- vasanthan
would you help me to convert byte array to image in reactjs
- shivam gupta
Thx a lot
- dfds