- Log in to:
- Community
- DigitalOcean
- Sign up for:
- Community
- DigitalOcean

Java Random class is used to generate a series of random numbers.
Java Random Class
Randomclass is part of java.util package.- An instance of java Random class is used to generate random numbers.
- This class provides several methods to generate random numbers of type integer, double, long, float etc.
- Random number generation algorithm works on the seed value. If not provided, seed value is created from system nano time.
- If two Random instances have same seed value, then they will generate same sequence of random numbers.
- Java Random class is thread-safe, however in multithreaded environment it’s advised to use
java.util.concurrent.ThreadLocalRandomclass. - Random class instances are not suitable for security sensitive applications, better to use
java.security.SecureRandomin those cases.

Java Random Constructors
Java Random class has two constructors which are given below:
Random(): creates new random generatorRandom(long seed): creates new random generator using specified seed
Java Random Class Methods
Let’s have a look at some of the methods of java Random class.
nextBoolean(): This method returns next pseudorandom which is a boolean value from random number generator sequence.nextDouble(): This method returns next pseudorandom which is double value between 0.0 and 1.0.nextFloat(): This method returns next pseudorandom which is float value between 0.0 and 1.0.nextInt(): This method returns next int value from random number generator sequence.- nextInt(int n): This method return a pseudorandom which is int value between 0 and specified value from random number generator sequence.
Java Random Example
Let’s have a look at the below java Random example program.
package com.journaldev.examples;
import java.util.Random;
/**
* Java Random Number Example Program
*
*/
public class RandomNumberExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//initialize random number generator
Random random = new Random();
//generates boolean value
System.out.println(random.nextBoolean());
//generates double value
System.out.println(random.nextDouble());
//generates float value
System.out.println(random.nextFloat());
//generates int value
System.out.println(random.nextInt());
//generates int value within specific limit
System.out.println(random.nextInt(20));
}
}
Output of the above program is:
false
0.30986869120562854
0.6210066
-1348425743
18
Check this post for more about Java Radom Number Generation.
Generate Random Number using Seed
There are two ways we can generate random number using seed.
Random random = new Random(long seed);
Random random1 = new Random();
random1.setSeed(seed);
The seed is the initial value of the internal state of the pseudorandom number generator which is maintained by method next(int).
package com.journaldev.examples;
import java.util.Random;
/**
* Java Random Number Using Seed Example Program
*
* @author pankaj
*
*/
public class RadomSeedExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//using constructor
Random random = new Random(100);
System.out.println("Using Constructor");
System.out.println(random.nextInt());
//using method
Random random2 = new Random();
random2.setSeed(200);
System.out.println("Using Method");
System.out.println(random2.nextInt());
}
}
Output of the above program is:
Using Constructor
-1193959466
Using Method
-1133938638
What if we pass same seed to two different random number generators? Let’s have a look at the below program and see what happen if we pass same seed to two different random number generators.
package com.journaldev.examples;
import java.util.Random;
/**
* Java Random Number Using Same Seed Example Program
*
*/
public class RandomNumberSameSeedExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//initialize two random number generators using same seed
Random random1 = new Random(100);
Random random2 = new Random(100);
System.out.println(random1.nextInt());
System.out.println(random2.nextInt());
}
}
Output of the above program is:
-1193959466
-1193959466
We can see that it will generate same random number if we pass same seed to two different random number generators.
Java 8 Random Class Methods
As you can see from above image, there are many new methods added in Java 8 to Random class. These methods can produce a stream of random numbers. Below is a simple program to generate a stream of 5 integers between 1 and 100.
package com.journaldev.random;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.stream.IntStream;
public class JavaRandomExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Random random = new Random();
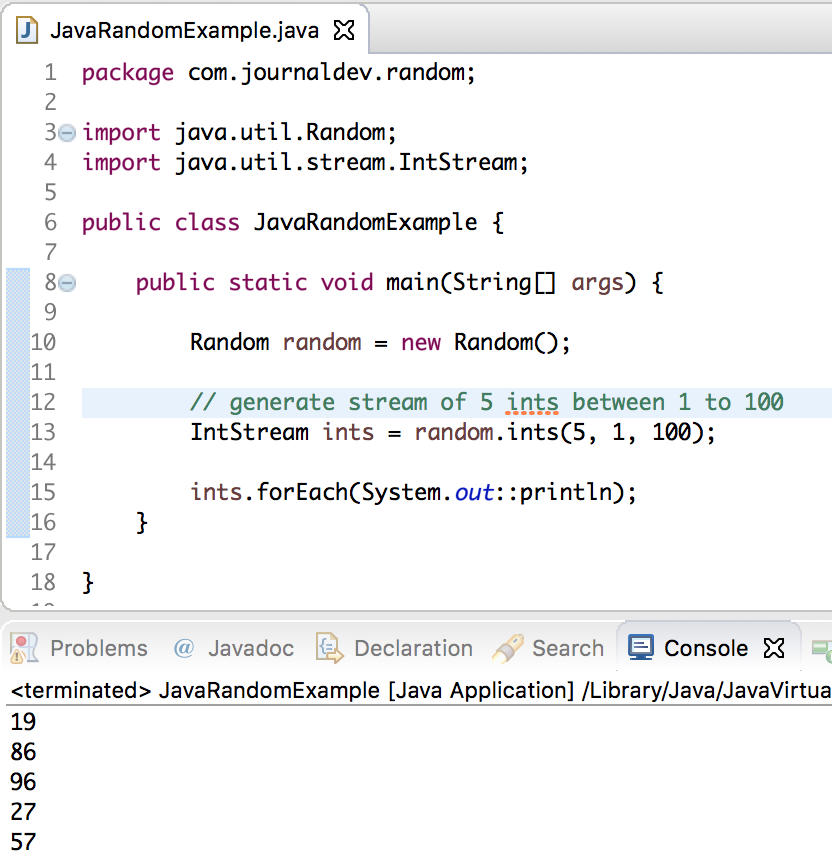
// generate stream of 5 ints between 1 to 100
IntStream ints = random.ints(5, 1, 100);
ints.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
 That’s all for a quick roundup on Java Random Class. Reference: API Doc
That’s all for a quick roundup on Java Random Class. Reference: API Doc
Thanks for learning with the DigitalOcean Community. Check out our offerings for compute, storage, networking, and managed databases.
About the author
Java and Python Developer for 20+ years, Open Source Enthusiast, Founder of https://www.askpython.com/, https://www.linuxfordevices.com/, and JournalDev.com (acquired by DigitalOcean). Passionate about writing technical articles and sharing knowledge with others. Love Java, Python, Unix and related technologies. Follow my X @PankajWebDev
Still looking for an answer?
- Table of contents
- Java Random Class
Deploy on DigitalOcean
Click below to sign up for DigitalOcean's virtual machines, Databases, and AIML products.
Become a contributor for community
Get paid to write technical tutorials and select a tech-focused charity to receive a matching donation.
DigitalOcean Documentation
Full documentation for every DigitalOcean product.
Resources for startups and SMBs
The Wave has everything you need to know about building a business, from raising funding to marketing your product.
Get our newsletter
Stay up to date by signing up for DigitalOcean’s Infrastructure as a Newsletter.
New accounts only. By submitting your email you agree to our Privacy Policy
The developer cloud
Scale up as you grow — whether you're running one virtual machine or ten thousand.
Get started for free
Sign up and get $200 in credit for your first 60 days with DigitalOcean.*
*This promotional offer applies to new accounts only.
