- Log in to:
- Community
- DigitalOcean
- Sign up for:
- Community
- DigitalOcean

Today we will look at how to generate a random number in Java. Sometimes we need to generate random numbers in Java programs. For example, a dice game or to generate a random key id for encryption, etc.
Random Number Generator in Java
 There are many ways to generate a random number in java.
There are many ways to generate a random number in java.
- java.util.Random class can be used to create random numbers. It provides several methods to generate random integer, long, double etc.
- We can also use Math.random() to generate a double. This method internally uses Java Random class.
java.util.concurrent.ThreadLocalRandomclass should be used to generate random number in multithreaded environment. This class is part of Java Concurrent package and introduced in Java 1.7. This class has methods similar to Java Random class.java.security.SecureRandomcan be used to generate random number with strong security. This class provides a cryptographically strong random number generator. However, it’s slow in processing. So depending on your application requirements, you should decide whether to use it or not.
Java Random Number Generator
Let’s look at some examples to generate a random number in Java. Later on, we will also look at ThreadLocalRandom and SecureRandom example program.
1. Generate Random integer
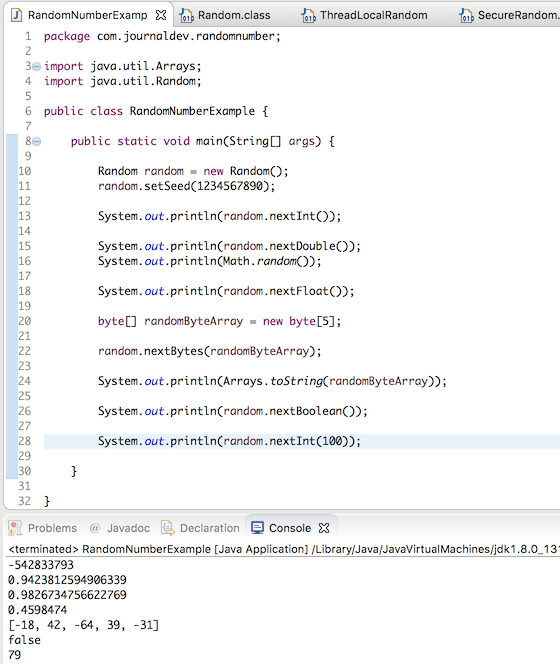
Random random = new Random();
int rand = random.nextInt();
Yes, it’s that simple to generate a random integer in java. When we create the Random instance, it generates a long seed value that is used in all the nextXXX method calls. We can set this seed value in the program, however, it’s not required in most of the cases.
//set the long seed value using Random constructor
Random random = new Random(123456789);
//set long seed value using setter method
Random random1 = new Random();
random1.setSeed(1234567890);
2. Java Random number between 1 and 10
Sometimes we have to generate a random number between a range. For example, in a dice game possible values can be between 1 to 6 only. Below is the code showing how to generate a random number between 1 and 10 inclusive.
Random random = new Random();
int rand = 0;
while (true){
rand = random.nextInt(11);
if(rand !=0) break;
}
System.out.println(rand);
The argument in the nextInt(int x) is excluded, so we have to provide argument as 11. Also, 0 is included in the generated random number, so we have to keep calling nextInt method until we get a value between 1 and 10. You can extend the above code to generate the random number within any given range.
3. Generate Random double
We can use Math.random() or Random class nextDouble method to generate random double number in java.
Random random = new Random();
double d = random.nextDouble();
double d1 = Math.random();
4. Generate Random float
Random random = new Random();
float f = random.nextFloat();
5. Generate Random long
Random random = new Random();
long l = random.nextLong();
6. Generate Random boolean
Random random = new Random();
boolean flag = random.nextBoolean();
7. Generate Random byte array
We can generate random bytes and place them into a user-supplied byte array using Random class. The number of random bytes produced is equal to the length of the byte array.
Random random = new Random();
byte[] randomByteArray = new byte[5];
random.nextBytes(randomByteArray);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(randomByteArray)); // sample output [-70, -57, 74, 99, -78]
8. ThreadLocalRandom in multithreaded environment
Here is a simple example showing ThreadLocalRandom usage in a multithreaded environment.
package com.journaldev.randomnumber;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadLocalRandom;
public class ThreadLocalRandomExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runnable runnable = new MyRunnable();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
Thread t = new Thread(runnable);
t.setName("MyRunnable-Thread-" + i);
t.start();
}
}
}
class MyRunnable implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
String threadName = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println(threadName + "::" + ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt());
}
}
Below is a sample output of my execution of the above program.
MyRunnable-Thread-0::-1744088963
MyRunnable-Thread-3::139405798
MyRunnable-Thread-1::1403710182
MyRunnable-Thread-2::-1222080205
MyRunnable-Thread-4::-185825276
We can’t set seed value for ThreadLocalRandom instance, it will throw UnsupportedOperationException. 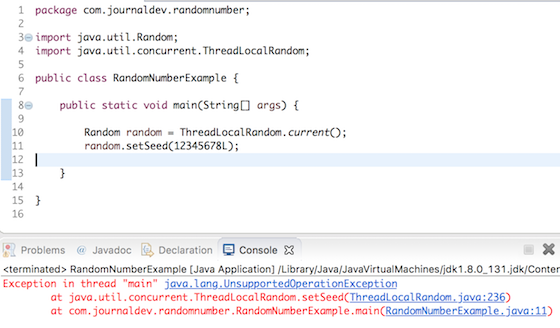 ThreadLocalRandom class also has some extra utility methods to generate a random number within a range. For example, to generate a random number between 1 and 10, we can do it like below.
ThreadLocalRandom class also has some extra utility methods to generate a random number within a range. For example, to generate a random number between 1 and 10, we can do it like below.
ThreadLocalRandom random = ThreadLocalRandom.current();
int rand = random.nextInt(1, 11);
ThreadLocalRandom has similar methods for generating random long and double values.
9. SecureRandom Example
You can use SecureRandom class to generate more secure random numbers using any of the listed providers. A quick SecureRandom example code is given below.
Random random = new SecureRandom();
int rand = random.nextInt();
System.out.println(rand);
That’s all about generating a random number in Java program.
You can download the example code from our GitHub Repository.
Thanks for learning with the DigitalOcean Community. Check out our offerings for compute, storage, networking, and managed databases.
About the author
Java and Python Developer for 20+ years, Open Source Enthusiast, Founder of https://www.askpython.com/, https://www.linuxfordevices.com/, and JournalDev.com (acquired by DigitalOcean). Passionate about writing technical articles and sharing knowledge with others. Love Java, Python, Unix and related technologies. Follow my X @PankajWebDev
Still looking for an answer?
Good article on Random number generation. I think you should add some example that how to create random number without using java class I mean beginner level program.
- Chaman Bharti
- Table of contents
- Random Number Generator in Java
- Java Random Number Generator
Deploy on DigitalOcean
Click below to sign up for DigitalOcean's virtual machines, Databases, and AIML products.
Become a contributor for community
Get paid to write technical tutorials and select a tech-focused charity to receive a matching donation.
DigitalOcean Documentation
Full documentation for every DigitalOcean product.
Resources for startups and AI-native businesses
The Wave has everything you need to know about building a business, from raising funding to marketing your product.
Get our newsletter
Stay up to date by signing up for DigitalOcean’s Infrastructure as a Newsletter.
New accounts only. By submitting your email you agree to our Privacy Policy
The developer cloud
Scale up as you grow — whether you're running one virtual machine or ten thousand.
Get started for free
Sign up and get $200 in credit for your first 60 days with DigitalOcean.*
*This promotional offer applies to new accounts only.
